💡 This study investigates the impact of a microbiome-directed complementary food (MDCF-2) on weight gain in 12–18-month-old Bangladeshi children with moderate acute malnutrition. Through metagenome-assembled genomes (MAGs), gene expression analysis, and glycan composition assessment, the study elucidates the microbiome targets and structure–function relationships of MDCF-2.
Childhood malnutrition is linked to perturbed postnatal development of the gut microbiome. This study focuses on MDCF-2, aiming to understand its impact on weight gain and microbiome modulation in malnourished children.
📍 Methods:
Participants: 12–18-month-old Bangladeshi children with moderate acute malnutrition.
Intervention: MDCF-2 vs. conventional ready-to-use supplementary food (RUSF) in a randomized controlled trial.
Analysis Techniques: Reconstruction of 1,000 bacterial genomes (MAGs), gene expression analysis of MAGs associated with weight gain, and glycan composition assessment using UHPLC–QqQ-MS.
Key Findings:
📌 𝘗𝘳𝘦𝘷𝘰𝘵𝘦𝘭𝘭𝘢 𝘤𝘰𝘱𝘳𝘪 MAGs and Ponderal Growth: Two 𝘗𝘳𝘦𝘷𝘰𝘵𝘦𝘭𝘭𝘢 𝘤𝘰𝘱𝘳𝘪 MAGs positively associated with weight-for-length Z score (WLZ) were principal contributors to MDCF-2-induced expression of metabolic pathways.
Positive correlation between 𝘗𝘳𝘦𝘷𝘰𝘵𝘦𝘭𝘭𝘢 𝘤𝘰𝘱𝘳𝘪 MAGs, their carbohydrate-active enzymes, and in vitro growth in medium containing glycans from MDCF-2.
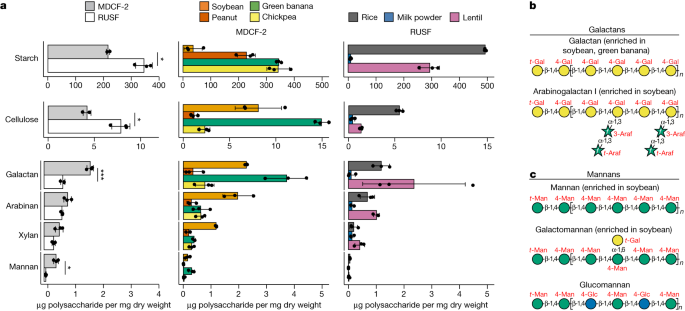
📌 Glycan Composition Analysis: MDCF-2 contains more galactans and mannans than RUSF. Statistically significant changes in glycan composition identified in the faeces of children consuming MDCF-2, emphasizing its impact on microbiome metabolism.
📌 Microbiome Repair and Diet Modification: MDCF-2 ‘kick starts’ a microbiome response, with changes in expressed metabolic functions of key growth-associated bacterial strains, such as 𝘗𝘳𝘦𝘷𝘰𝘵𝘦𝘭𝘭𝘢 𝘤𝘰𝘱𝘳𝘪. Background diet modifies this response, as reflected in higher levels of microbial metabolic products in the faeces of children with upper-quartile WLZ responses.
📍 This study sheds light on the microbiome targets and structure–function relationships of MDCF-2, emphasizing the role of 𝘗𝘳𝘦𝘷𝘰𝘵𝘦𝘭𝘭𝘢 𝘤𝘰𝘱𝘳𝘪 MAGs in weight gain and glycan metabolism. The findings pave the way for microbiome-targeted therapeutic foods and offer avenues for further research in probiotics and synbiotics
Link to the article: http://tinyurl.com/3bbtaumr