Neurodegenerative diseases, particularly mild cognitive impairment (MCI) and dementia (D), are characterized by a decrease in cognitive skills, accompanied by neuroinflammation associated with an increase in intestinal permeability. In younger people, inflammation is a fundamental response to cope with internal and external damaging agents; however, in later life, it can be detrimental, contributing to the development of various age-related chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Dysbiosis in gut microbiota increases serum levels of tau protein, β-amyloid, and LPS as well as stool curli protein during mild cognitive impairment and dementia, these are associated with an increase in
Link to the article: bit.ly/3onl8FC
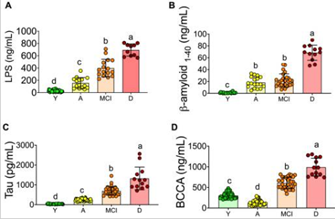
Serum biomarkers associated with inflammation and neurodegeneration in serum of young and aging adults. Lipopolysaccharide (A). Tau protein (B), β-amyloid protein 1–40 (C), and total branched-chain amino acids (D) in serum.
Published On: /05/2023