💡 The psychological health risks associated with manned deep-space exploration and long-term closed environments have prompted research into innovative approaches to maintain and improve the mental well-being of crew members.
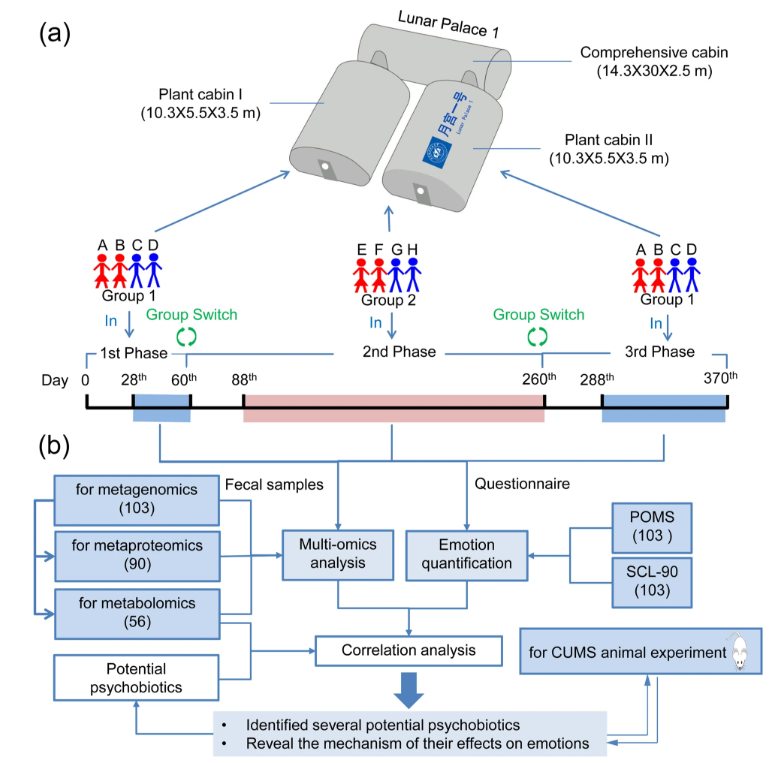
This study leveraged the unique setting of the “Lunar Palace 365” mission, a year-long isolation study, to investigate the correlation between gut microbiota and psychological changes. Through comprehensive multiomics analyses, the study identified four potential psychobiotics—𝘉𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘰𝘪𝘥𝘦𝘴 𝘶𝘯𝘪𝘧𝘰𝘳𝘮𝘪𝘴, 𝘙𝘰𝘴𝘦𝘣𝘶𝘳𝘪𝘢 𝘪𝘯𝘶𝘭𝘪𝘯𝘪𝘷𝘰𝘳𝘢𝘯𝘴, 𝘌𝘶𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘶𝘮 𝘳𝘦𝘤𝘵𝘢𝘭𝘦, 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘍𝘢𝘦𝘤𝘢𝘭𝘪𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘶𝘮 𝘱𝘳𝘢𝘶𝘴𝘯𝘪𝘵𝘻𝘪𝘪—that demonstrated a significant association with positive moods and a reduction in negative moods.
📍 Key Findings:
📌 Identification of Potential Psychobiotics: 𝘉𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘰𝘪𝘥𝘦𝘴 𝘶𝘯𝘪𝘧𝘰𝘳𝘮𝘪𝘴, originally isolated from healthy breast-fed infants, demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects and improved metabolic and immune dysfunction. 𝘙𝘰𝘴𝘦𝘣𝘶𝘳𝘪𝘢, 𝘌𝘶𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘶𝘮, 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘍𝘢𝘦𝘤𝘢𝘭𝘪𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘶𝘮, being abundant in the human gut microbiota, were associated with the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) through the fermentation of dietary fibers.
📌 Functional Mechanisms of Psychobiotics on Mood: Psychobiotics influenced mood through three main pathways related to nervous system functions: Fermentation of dietary fibers to produce SCFAs (e.g., butyric and propionic acids). Regulation of amino acid metabolism pathways (e.g., conversion of glutamic acid to gamma–aminobutyric acid; conversion of tryptophan to serotonin, kynurenic acid, or tryptamine). Regulation of other pathways, including taurine and cortisol metabolism.
📌 Metabolic Pathways Associated with Psychobiotics: Metagenomic and metaproteomic analyses revealed pathways related to polysaccharide metabolism and SCFA production. Metabolomic analysis showed positive correlations between potential psychobiotics and metabolites such as pyruvate, propionic acid, butyric acid, GABA, tryptamine, serotonin, and KYNA.
📌 Animal Experiments Confirming Psychobiotic Effects: Behavioral tests on rats subjected to chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) demonstrated that potential psychobiotics reduced depression- and anxiety-like behaviors. Metabolite analysis in rats supported the multiomics findings, indicating increased SCFA production and modulation of neurotransmitter pathways.
📌 Additional Mechanisms of Psychobiotics: Psychobiotics were found to produce other small molecule metabolites (e.g., histamine, L-glutamine, and noradrenaline hydrochloride). Psychobiotics reduced immune factors and biomarkers associated with intestinal permeability and inflammation, suggesting a positive impact on the enteric nervous system (ENS) and central nervous system (CNS).
📌 This study provides a significant step toward understanding the role of gut microbiota in maintaining mental health during extended space missions. The identified potential psychobiotics offer promising avenues for developing microbiota-based interventions to safeguard crew mental health during future long-term human space expeditions to the moon or Mars. Additionally, the findings contribute valuable insights for the potential application of psychobiotics in neuropsychiatric treatments on Earth.
Link to the article : http://tinyurl.com/y2zsawum