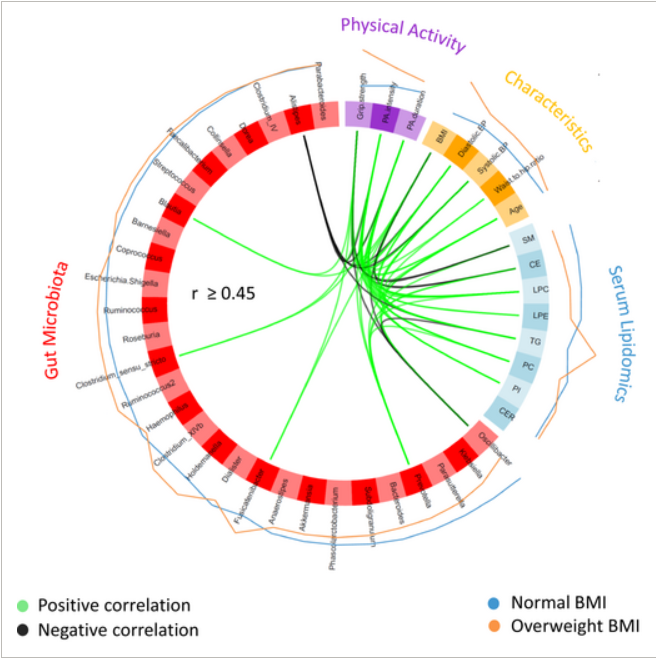
Physical activity is associated with various preventative and therapeutic health effects against inflammatory, cardiometabolic diseases and help induce positive changes in the gut microbiota composition and in the microbial metabolites produced in the gastrointestinal tract. It is also recognized as an important environmental factor associated with gut microbiota adaptation. Here, researchers evaluate the effects of body mass index (BMI) on physical activity and muscle/hand-grip strength-induced intestinal microbiome compositional alterations among middle-aged adult individuals. Study findings show that BMI significantly influences physical activity-induced alterations in intestinal microbiota composition, and ex-specific associations with hand-grip strength and the microbiota were also found, specifically for
Link to the article: rb.gy/cnzghu
Published On: 27/03/2023