💡This study aims to comprehensively investigate gut microbiota dysbiosis and metabolite levels in very low or extremely low birth weight (VLBW/ELBW) infants with white matter injury (WMI).
📌Utilizing a multi-omics approach, including 16S rRNA gene sequencing, liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), and diffusion tension imaging (DTI), the study explores the intricate relationships between gut microbiota, metabolites, and the structural integrity of white matter in the brains of preterm infants.
Methods:
A cohort of 71 preterm infants with gestational age < 32 weeks and weight < 1.5 kg was enrolled in this study. Fecal samples were collected at days zero, 14, and 28 after admission to the intensive care unit. Brain scans via magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and DTI were conducted at a corrected gestational age of 37–40 weeks. Based on MRI results, infants were categorized into WMI and non-WMI groups. A multi-omics approach involved 16S rRNA gene sequencing, LC-MS/MS metabolomics, and DTI to identify biomarkers associated with WMI.
Key Findings:
📌 Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis: WMI infants exhibited increased abundance of 𝘚𝘵𝘢𝘱𝘩𝘺𝘭𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴, 𝘈𝘤𝘪𝘯𝘦𝘵𝘰𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳, 𝘉𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘰𝘪𝘥𝘦𝘵𝘦𝘴, 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘈𝘤𝘵𝘪𝘯𝘰𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘢. Abnormal colonization of 𝘚𝘵𝘢𝘱𝘩𝘺𝘭𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘈𝘤𝘵𝘪𝘯𝘰𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘢 was observed within the first month of life in WMI infants.
📌 Species-Level Abundance: 𝘚. 𝘤𝘢𝘱𝘳𝘢𝘦 was significantly higher in the WMI group, while 𝘉. 𝘭𝘰𝘯𝘨𝘶𝘮 was decreased. 𝘒𝘭𝘦𝘣𝘴𝘪𝘦𝘭𝘭𝘢 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘗𝘢𝘳𝘢𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘰𝘪𝘥𝘦𝘴 were enriched in the meconium of the WMI group, indicating potential early brain damage.
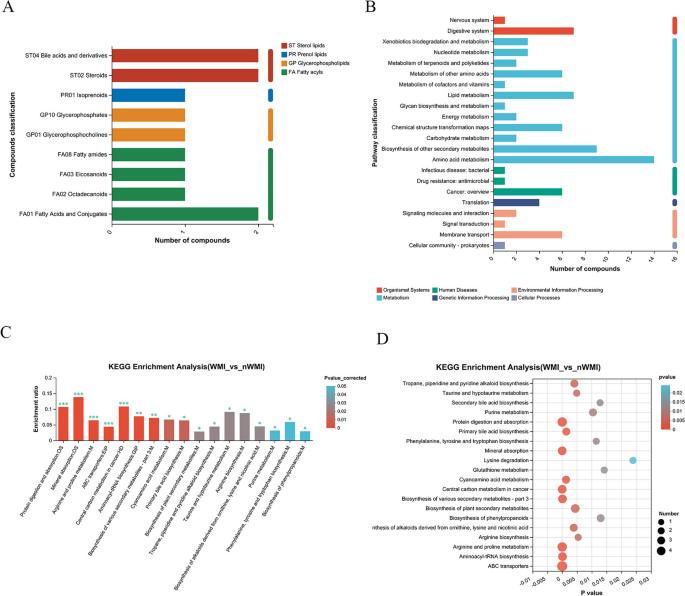
📌 Metabolite Profiling: WMI infants showed significant downregulation in metabolite pathways related to taurine, hypotaurine, arginine biosynthesis, and primary bile acids. Cinobufagin, didesethylflurazepam, N-acetylneuraminic acid, and adenosine 3’-monophosphate were upregulated, while cholic acid and allocholic acid were downregulated in the WMI group.
📌 Correlation with Brain Structure: 𝘉. 𝘭𝘰𝘯𝘨𝘶𝘮 negatively correlated with occipital white matter apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), suggesting a protective effect. Metabolites like cinobufagin were positively correlated with ADC values, indicating potential brain damage.
📍 This pioneering study unveils severe gut microbiota dysbiosis in VLBW/ELBW infants with WMI, highlighting associations between specific microbial taxa, altered metabolite profiles, and compromised white matter integrity. The findings underscore the potential role of the microbiota-gut-brain axis in the pathogenesis of WMI and open avenues for further research and therapeutic interventions targeting early gut colonization to prevent or mitigate WMI in preterm infants.
Link to the article : https://tinyurl.com/mw2nez7m