💡 This study revolves around the synthesis and testing of new Quaternary Ammonium and Phosphonium salts and their effectiveness against 𝘚𝘵𝘢𝘱𝘩𝘺𝘭𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴 𝘢𝘶𝘳𝘦𝘶𝘴, a prevalent bacteria known for its antibiotic resistance property.
📍 The objective of this research is to determine the antibacterial efficacy of these newly synthesized compounds differing in cation type and alkyl chain length in combating antibiotic-resistant 𝘚𝘵𝘢𝘱𝘩𝘺𝘭𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴 𝘢𝘶𝘳𝘦𝘶𝘴.
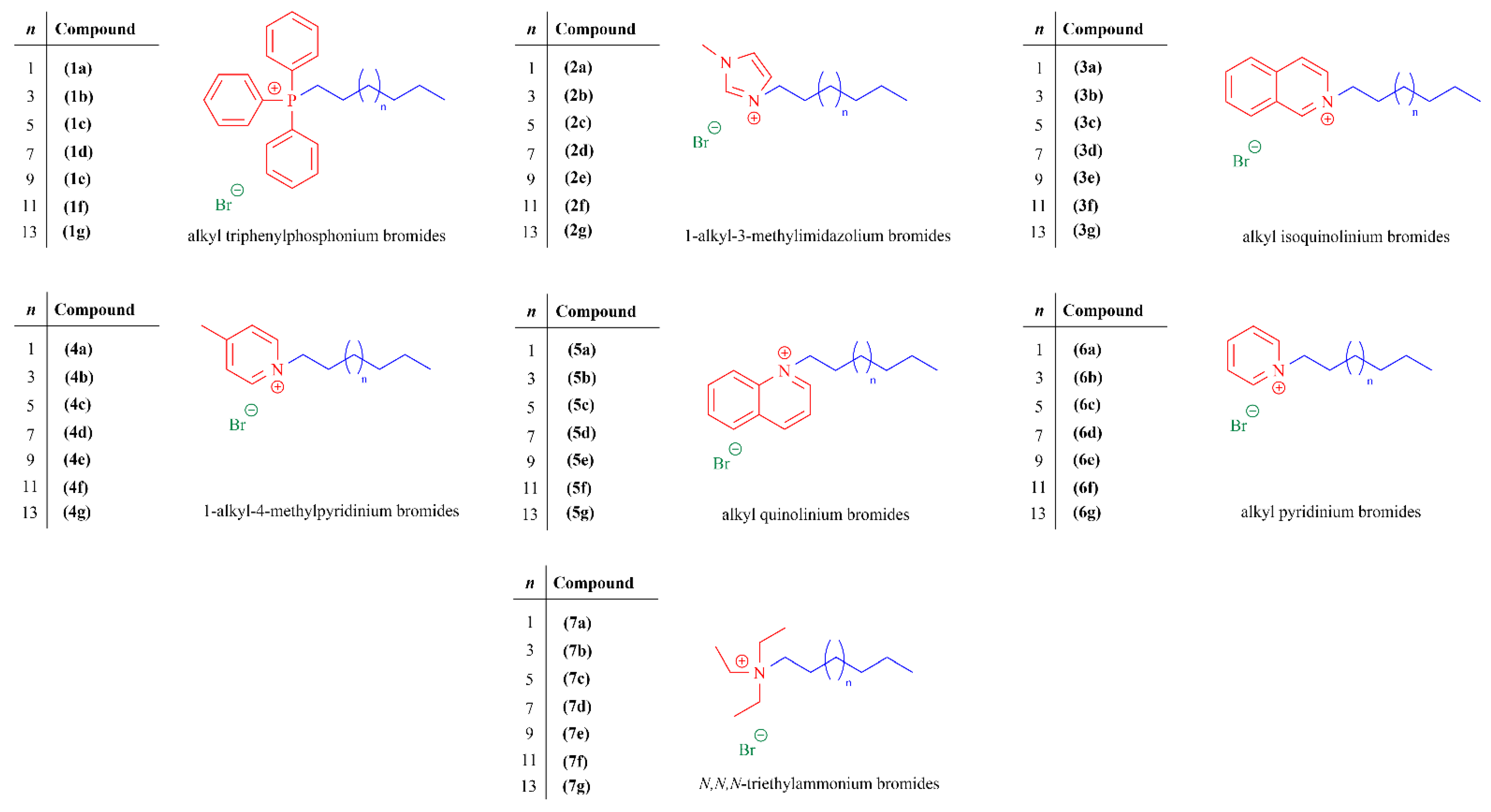
📌 The novel compounds were synthesized through two general procedures. Specific techniques such as Nuclear Magnetic Resonance were used to confirm the structures of the synthesized compounds.
📌 The synthesis yielded 49 structurally related QHSs with high purity and in moderate to high yields. The SAR study highlighted the role of cation types and alkyl chain length in antibacterial activity. Some compounds exhibited strong bactericidal effects at low µg/mL concentrations, with triphenylphosphonium and methylimidazolium derivatives showing superior activity. An optimal chain length of C14 was identified for peak antibacterial efficiency.
– Novel quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts displayed significant antibacterial potential.
– Compounds 1e, 3e, and 5e showed high efficacy against 𝘚𝘵𝘢𝘱𝘩𝘺𝘭𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴 𝘢𝘶𝘳𝘦𝘶𝘴 at low concentrations.
– Some QHSs presented a favorable safety profile with minimal cytotoxicity on HepG2 cells.
– There is a delicate balance between cation structure, alkyl chain length, and antibacterial activity.
– Optimal antibacterial activity was observed at a specific range of alkyl chain length, beyond which efficacy declined.
– Findings challenge the view that increased lipophilicity uniformly improves antibacterial potency.
📌 The study concluded that certain quaternary ammonium and phosphonium salts present promising characteristics in the fight against multidrug-resistant bacterial strains, particularly 𝘚𝘵𝘢𝘱𝘩𝘺𝘭𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴 𝘢𝘶𝘳𝘦𝘶𝘴. Through a detailed structure-activity relationship analysis, the research established a foundation for understanding how modifications in chemical structure impact antibacterial performance. It was determined that quaternary salts with specific structural attributes could be developed into new agents for combating resistant infections.
These findings underscore the potential of QHSs as a platform for future antimicrobial drug design, emphasizing the need for further investigation to optimize these compounds for clinical use.
Link to the article : http://tinyurl.com/h445tt2e