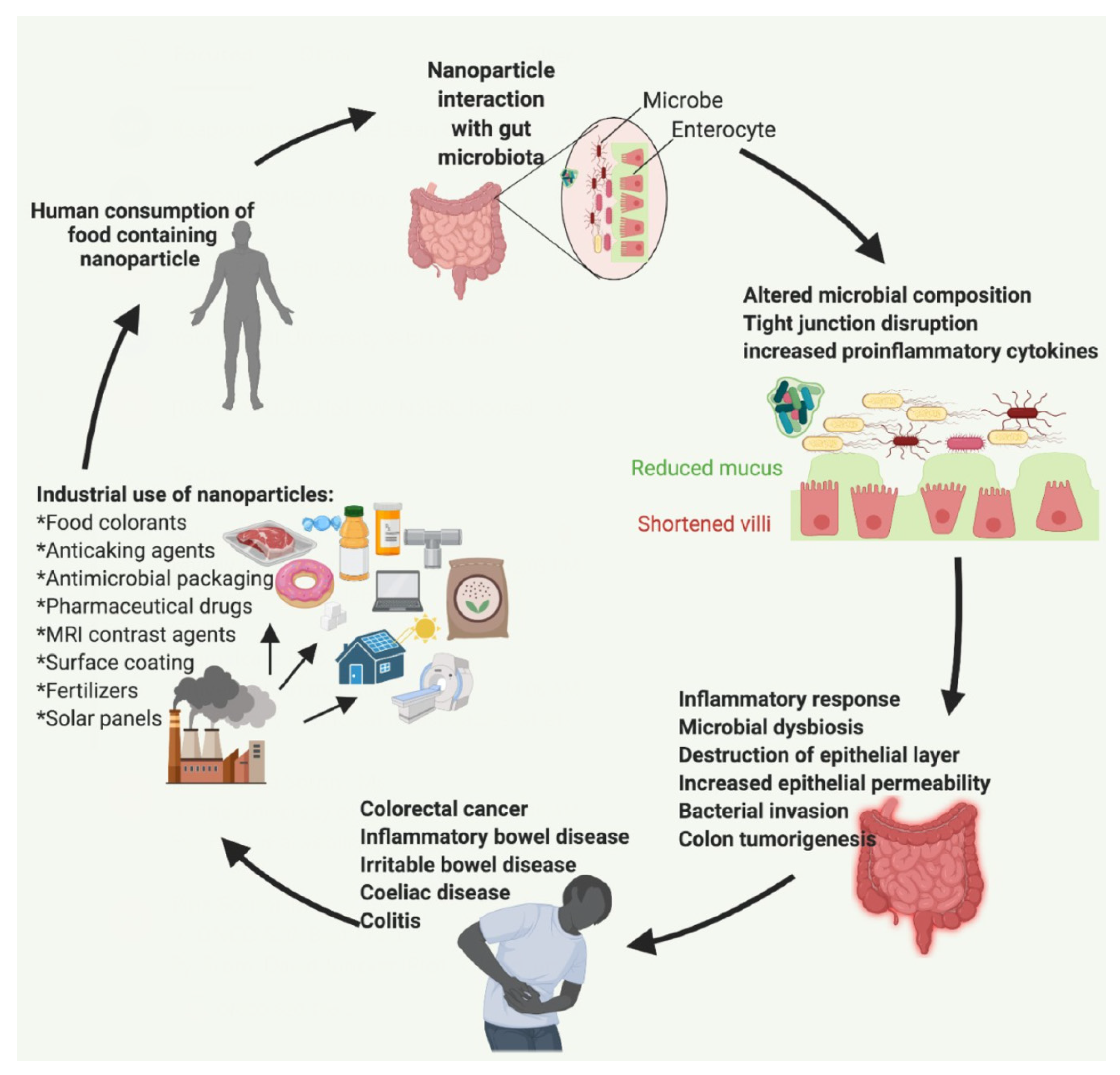
Gut microbiota modifications due to various environmental factors are associated with impaired gut barrier integrity, increasing bacterial translocation and contributing to low-grade inflammation. The host and the gut microbiota can alter clinical outcomes of various non-communicable diseases, such as autism spectrum disorders, ischemia-reperfusion, and kidney diseases. The modulation of gut microbiota through prebiotics, probiotics, and fecal microbiota transplant has garnered interest to alleviate
intestinal barrier dysfunctions. Gut microbiota and gut barrier integrity bridge many, distant, host zones through microbial metabolite production and the immune system. Authors here, compiled fifteen original papers and nine reviews, aiming to dissect the gut microbiota/gut barrier interactions, outlining their potential role in health and diseases and explore the ways in which interactions between the host and the gut microbiota can alter clinical outcomes of various non-communicable diseases. This study does endorse the hypothesis of Gut-Revival which Microvioma is pursuing.
Link to the article: bit.ly/3KWrovb
Published On: /04/2023