💡 The study was aimed at understanding the inhibitory effects of a Desmethyl-phosphinothricin Dipeptide Derivative on the growth of the bacterial strains 𝘌𝘴𝘤𝘩𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘤𝘩𝘪𝘢 𝘤𝘰𝘭𝘪 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘉𝘢𝘤𝘪𝘭𝘭𝘶𝘴 𝘴𝘶𝘣𝘵𝘪𝘭𝘪𝘴.
📌 Researchers synthesized a Desmethylphosphinothricin Dipeptide derivative and tested its antibacterial activity using controlled growth studies and monitoring against 𝘌𝘴𝘤𝘩𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘤𝘩𝘪𝘢 𝘤𝘰𝘭𝘪 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘉𝘢𝘤𝘪𝘭𝘭𝘶𝘴 𝘴𝘶𝘣𝘵𝘪𝘭𝘪𝘴.
📌 L-Leu-D, L-Glu-γ-PH, a dipeptide derivative of desmethylphosphinothricin or Glu-γ-PH, was synthesized and found to inhibit 𝘌𝘴𝘤𝘩𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘤𝘩𝘪𝘢 𝘤𝘰𝘭𝘪 𝘢𝘯𝘥 growth effectively.
The synthesized dipeptide exhibited superior antibacterial activity compared to its phosphonic and non-desmethylated analogues when assayed in a chemically defined minimal medium.
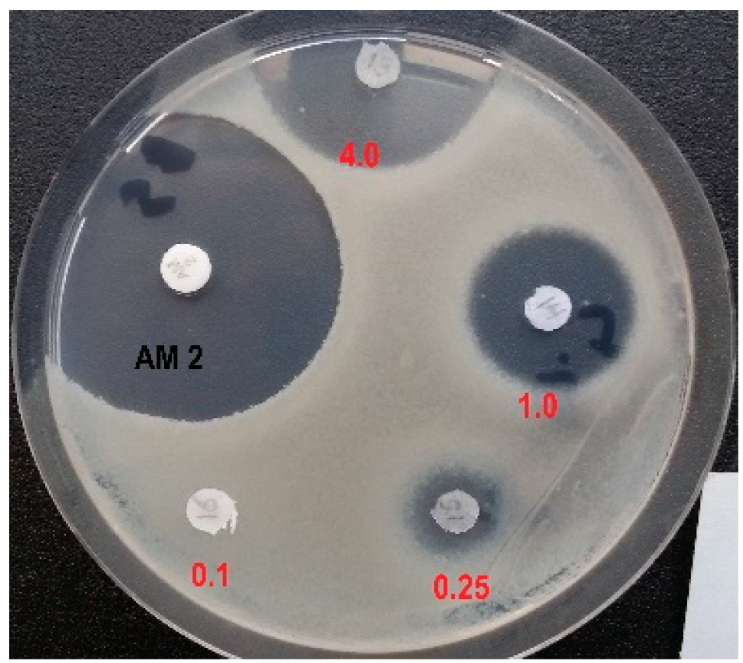
📌 Specifically, the dipeptide L-Leu-D, L-Glu-γ-PH showed significant antibacterial activity at a concentration of 2 µg/mL, which falls between the activity shown by the non-desmethylated (0.1 µg/mL) and phosphonic (80 µg/mL) analogues.
📌 The same dipeptide also showed comparable antibacterial properties to the well-known antibiotic amoxicillin when tested against Bacillus subtilis.
These results highlight the potential of the phosphinic pharmacophore for the development of novel antimicrobial drugs.
📍 This study contributes to antibiotic stewardship programs by offering a new potential direction for the development of antimicrobials. By investigating the antibacterial potential of phosphinic derivative dipeptides, the study illuminates the utility of targeting bacterial central metabolism, thus providing an innovative technique for managing multidrug resistance in bacteria.
Link to the article : https://bit.ly/45BCHBk