💡 The study investigates the potential health effects of long-term exposure to 4.9 GHz radiofrequency (RF), a frequency used in 5G communication, on the fecal microbiome and metabolome profiles in adult male C57BL/6 mice. The aim is to assess the influence of RF fields on gut microbiota and metabolic processes, considering the growing concern about the impact of RF on human health.
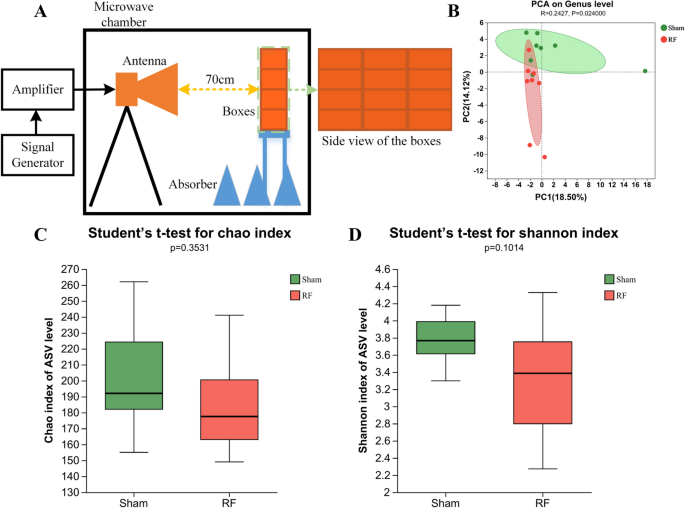
📍 Experimental Design: Mice were exposed to 4.9 GHz RF for three weeks, 1 hour per day, at an average power density of 50 W/m². Fecal samples were collected post-exposure for analysis of gut microorganisms using 16S rRNA gene sequencing and metabolites using LC–MS (liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry).
📌 Microbiota Alterations: Results revealed significant alterations in the intestinal microbial compositions in the RF-exposed group. Reduced microbial diversity and changes in community distribution were observed, indicating a potential impact of 4.9 GHz RF exposure on gut microbiota.
📌 Microbial Abundance Changes: 𝘍𝘪𝘳𝘮𝘪𝘤𝘶𝘵𝘦𝘴 showed a marked increase in relative abundance, while 𝘉𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘰𝘪𝘥𝘦𝘵𝘦𝘴 exhibited a non-significant decrease, resulting in a decreased 𝘉𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘰𝘪𝘥𝘦𝘵𝘦𝘴/𝘍𝘪𝘳𝘮𝘪𝘤𝘶𝘵𝘦𝘴 (B/F) ratio. 𝘓𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘰𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘪𝘭𝘭𝘶𝘴, a probiotic within 𝘍𝘪𝘳𝘮𝘪𝘤𝘶𝘵𝘦𝘴, significantly increased after RF exposure, suggesting a potential gut-protective role. 𝘔𝘶𝘳𝘪𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘶𝘭𝘢𝘤𝘦𝘢𝘦 showed a significant reduction, consistent with previous findings associating it with radiation exposure.
📌 Metabolomic Profiling: Metabolomics identified 258 significantly differentially abundant metabolites in the RF-exposed group. These metabolites were mainly annotated into amino acid metabolic pathways. Key metabolites involved in tryptophan metabolism, such as Pyrroline hydroxycarboxylic acid and Indole-3-acetamide, showed extremely significant differences.
📌 Metabolites with Neuroregulatory Functions:
N-Acetylaspartylglutamic acid (NAAG), a neuropeptide with neuroprotective effects, significantly reduced in the RF-exposed group. This reduction may be associated with RF-induced depression-like behavior observed in previous studies. Decreased Indole-3-acetamide may contribute to insufficient activation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) and further impact neuroendocrine and intestinal immune responses.
📌 Impact on Amino Acid Metabolism: Differential metabolites were mainly enriched in arginine and proline metabolism pathways, potentially causing damage to the body by affecting protein production. The role of amino acids in biological oxidation, cell metabolism, and protein synthesis may contribute to changes in immune regulation, gastrointestinal function, and overall body metabolism.
📌 Gut Microbiota-Metabolite Interactions: Functional correlation analysis showed significant correlations between changes in gut microbiota genera and alterations in fecal metabolites. 𝘉𝘢𝘤𝘪𝘭𝘭𝘶𝘴 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘉𝘪𝘧𝘪𝘥𝘰𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘶𝘮 were notably correlated with most differential metabolites, suggesting their significant contributions to metabolic disturbances during RF exposure.
📍 This study provides evidence that 4.9 GHz RF exposure induces significant alterations in the gut microbiota and metabolic profiles of mice. The observed changes in microbial diversity, abundance, and metabolites, particularly those with neuroregulatory functions, suggest a potential link between RF exposure and physiological effects. Further investigations are needed to elucidate the mechanisms behind these observations and determine the biological significance of the observed phenomena.
Link to the Study : http://tinyurl.com/bdeuh8pw