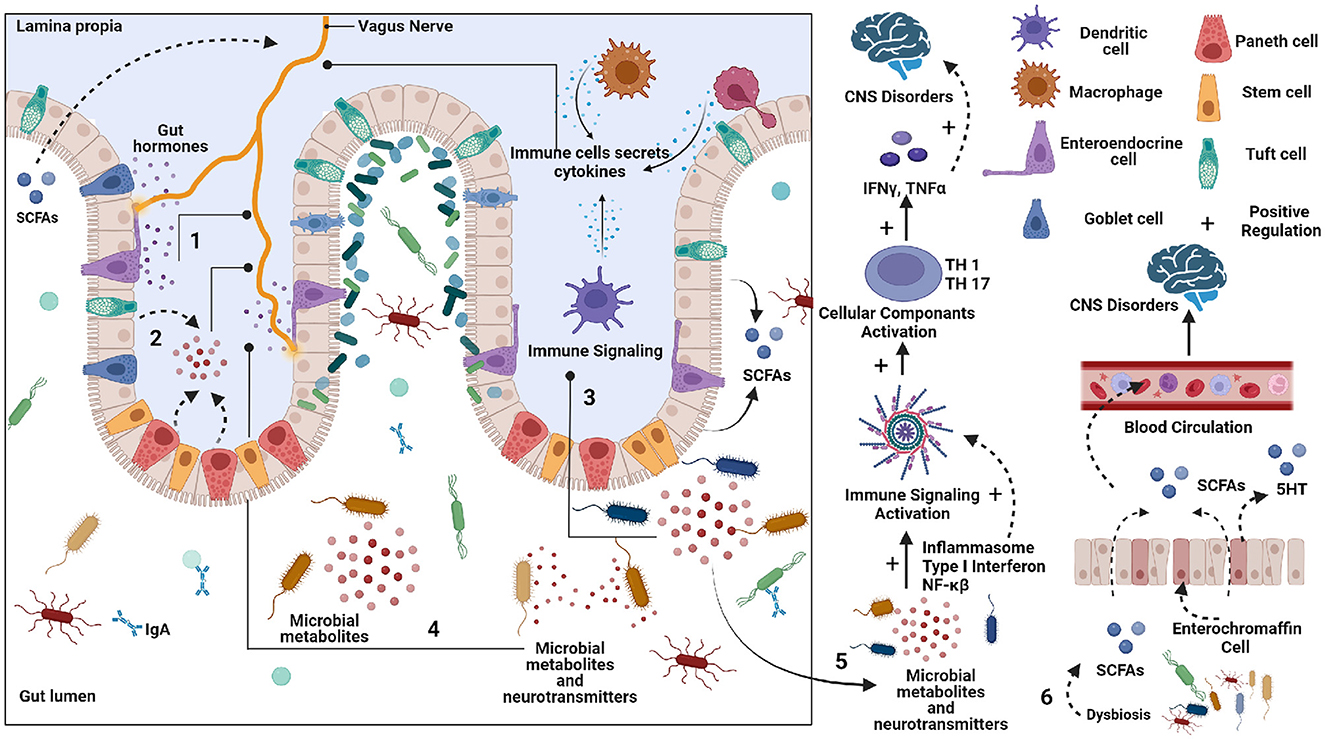
Gut microbes and the brain communicate bidirectionally through various neuroendocrine, neuroimmune and neural connections like the vagus nerve. Short-chain fatty acids are key molecules in microbiota-gut-brain interaction. Microbial dysbiosis is associated with neurodegenerative diseases which the authors in this study, explore the metabolic role of microbial dysbiosis in its pathogenesis and progression. They also performed a comparative analysis of microbial composition changes occurring in Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), Multiple sclerosis (MS), and Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Their research showed a high resemblance of microbial dysbiosis signatures between AD, PD, and MS, whereas ALS appeared dissimilar. The study also provides insights on imbalances in neurotransmitter precursor synthesis, with decreased representation of tryptophan and histamine and lower representation of the neuroprotective compound spermidine in the genome of microbes with an elevated population.
Link to the article: bit.ly/3A7iWEC
Published On: /04/2023