Hyperthermia induced by phenethylamines like 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) can lead to severe health complications and death. The sympathetic nervous system’s activation and norepinephrine release have been implicated in this condition. The gut microbiome and its production of bile acids (BAs) may also play a critical role in phenethylamine-induced hyperthermia (PIH).
This study explores the hypothesis that BAs produced by gut bacteria contribute to PIH, examining changes in serum BA levels and gut microbiome composition following MDMA treatment in antibiotic-treated and control rats.
Methods
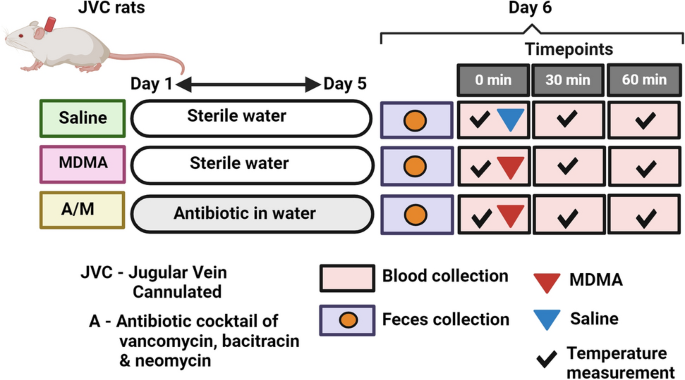
This study employed a cross-sectional approach with 92 rats divided into antibiotic-treated and control groups. Rats received antibiotics in drinking water for five days before MDMA (20 mg/kg) administration. Serum levels of CA, CDCA, and DCA were measured 60 minutes post-MDMA treatment. Gut microbiome composition was analyzed using 16S rRNA sequencing, and functional gene content was inferred using the bioinformatic tool PICRUSt2.
Key Detailed Findings
- MDMA-Induced Hyperthermia: MDMA significantly increased body temperature in rats, correlating with decreased serum levels of primary bile acids (cholic acid [CA] and chenodeoxycholic acid [CDCA]) and secondary bile acid (deoxycholic acid [DCA]).
- Antibiotic Pretreatment Effects: Pretreatment with antibiotics (vancomycin, bacitracin, and neomycin) altered the gut microbiome, reduced BA levels, and induced a hypothermic response to MDMA instead of the usual hyperthermic response.
- Microbiome Alterations: Antibiotic treatment led to decreased gut microbiome diversity and significant changes in bacterial taxa. PICRUSt2 analysis indicated a reduction in bacterial genes associated with BA metabolism in the antibiotic-MDMA treated group.
- Functional Gene Abundance: The antibiotic-MDMA treated group showed an increased relative abundance of bile salt hydrolase (BSH) genes but a depletion of genes in the bai operon, which are involved in secondary BA production.
Link to the study : https://tinyurl.com/p5zjuhes