Brain Awareness Week 2023
Series 6 of 7
How To Improve And Maintain The Brain-Gut Axis
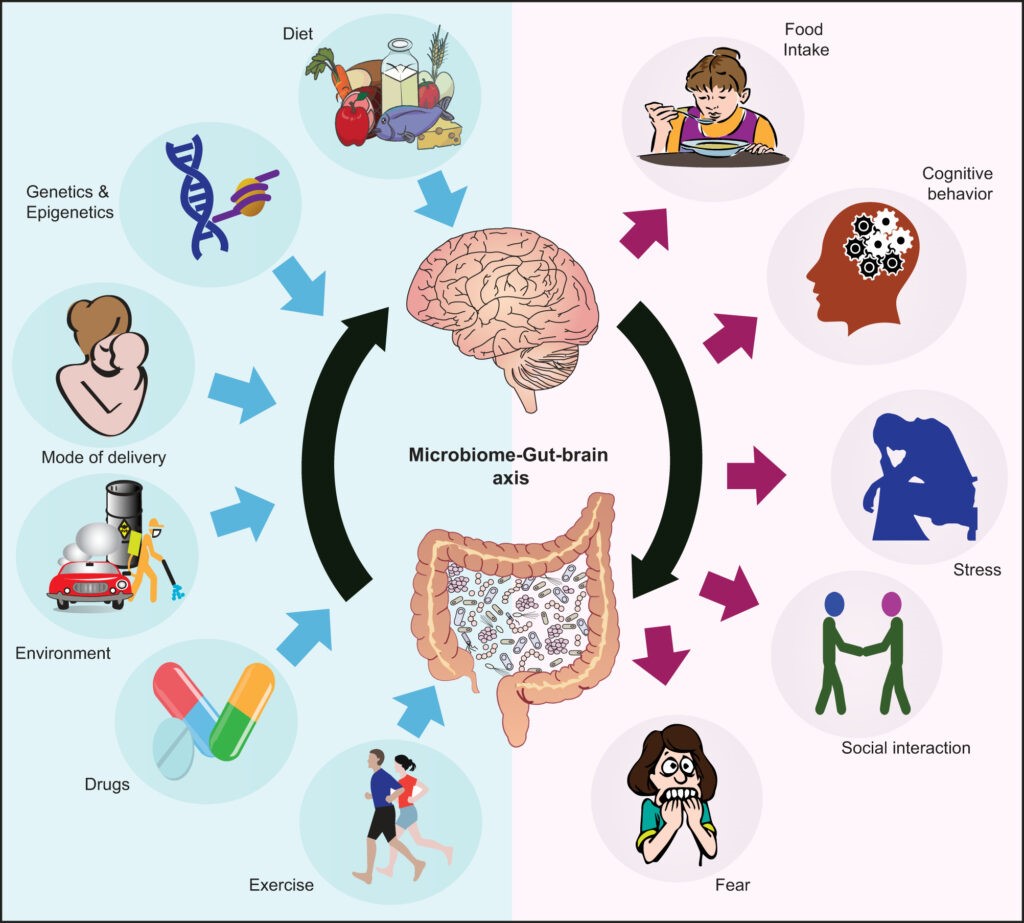
The gut-brain axis is a highly complex system that connects the brain and the gut. It is responsible for regulating a range of physiological processes, including mood, digestion, and immune function. Gut dysbiosis can have a range of negative effects on digestion and overall health, including inflammation and the disruption of the gut-brain axis leading to gastrointestinal diseases or can aggravate neurodegenerative disorders.
A healthy diet (probiotics, prebiotics, and postbiotics), phytochemicals, regular exercise, well-maintained sleep-cycle can promote increased microbial diversity and production of short-chain fatty acids, neurotransmitters and other bioactive compounds with beneficial physiological effects from gastrointestinal and metabolic health to brain processes.
- The gut-brain axis is highly influenced by our diet, lifestyle, and overall health.
- A well-balanced nutritious diet is considered as an amendable factor that can help to protect against the onset and manifestation of mental health disorders by controlling the gut-brain axis.
- The gut microbiota may be a key mediator of dietary effects on mental health, although diet is also known to be involved in brain functioning through other microbiota-independent mechanisms.
- Gut microbiome-targeted intervention strategies to promote the development and maintenance of a healthy brain.
- Gut microbes synthesize key neuroactive molecules such as the γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA), catecholamines (noradrenaline, norepinephrine, dopamine), serotonin (5-HT) and tryptophan metabolites and precursors.
- Gut bacteria can convert neurotransmitters precursors into active forms, such as the amino acid glutamate to GABA by Escherichia spp., while Lactobacillus spp. can stimulate the conversion of dietary tryptophan into 5-HT by enterochromaffin cells.
- These neuroactive molecules can interact with the autonomic nervous system or stimulate vagal sensory neurons in the gut leading to neuronal activation.
- Certain steps to improve and maintain a healthy gut-brain axis involve,
1. Eat a healthy diet
Helps promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, which can, in turn, positively impact your brain health.
2. Stay hydrated
Helpa reduce inflammation in the gut and improve overall immune function.
3. Exercise regularly
Helps in promoting the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, reduce inflammation, and improve cognitive function.
4. Manage stress
Maintain a well-balanced sleep-cycle with stress-reducing activities.
Further reading:
- Diet and the Microbiota–Gut–Brain Axis: Sowing the Seeds of Good Mental Health : rb.gy/euqc0f
- Towards Tailored Gut Microbiome-Based and Dietary Interventions for Promoting the Development and Maintenance of a Healthy Brain : rb.gy/5fyvlc
- Diet and the microbiota–gut–brain-axis: a primer for clinical nutrition : t.ly/8VW5
- How to Increase Your Gut Brain Connection Through Diet :
t.ly/EFe- - The Gut-Brain Connection: How it Works and The Role of Nutrition : t.ly/kIQFO
Source Link: t.ly/EJZK
Published On: 18/03/2023