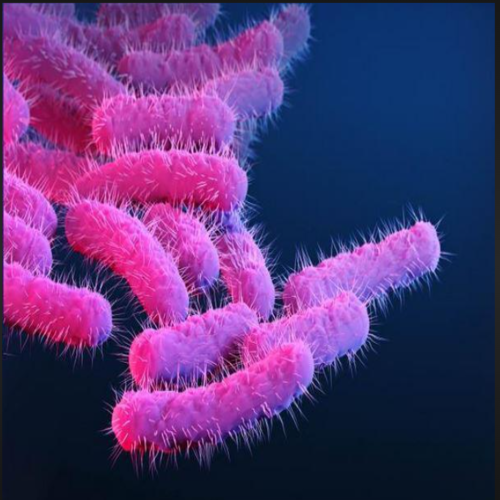
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention have detected an increase in the extensively drug-resistant (XDR) shigella strains, causing shigellosis, a major emerging public health issue. The highly contagious shillega bacterial infection causes inflammatory diarrhea, fever, and stomach pain. There has been an increase in infections among the adult population, increasing from 0% in 2015 to 5% in 2022. All commonly used antibiotics will not work against XDR shigellabacteria — including azithromycin, ciprofloxacin, ceftriaxone, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and ampicillin. In case of severe illness, antimicrobial treatment is recommended by healthcare practitioners according to the antimicrobial stewardship guidelines. This global health threat, calls for an immediate action and increased monitoring of the rise of antimicrobial resistance.
Link to the article: bit.ly/3SMyzKg
Publishes On: 03/03/2023