Plant-based diets are gaining popularity worldwide, mainly due to their health benefits, environmental concerns, and religious following plant-based diets are lower in saturated fats and high in fiber and phytochemicals, leading to decreased risk of obesity, cardiovascular diseases, metabolic disorders, and neurodegenerative disorders .These diets have also been associated with increased short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), negatively correlated with pro-inflammatory cytokines. The positive health effects of SCFAs are myriad, including improved immunity against pathogens, blood–brain barrier integrity, provision of energy substrates, and regulation of critical functions of the intestine. Dietary composition appears to have long-term and acute effects on the gut microbiota ecosystem. The high level of SCFAs and trimethylamine N-oxide metabolites in the plasma of individuals under these diets indicate the role of the gut microbe as a modulator of the diet–host interaction. In this study, researchers have reviewed the existing literature to understand how certain diets lead to gut dysbiosis, negatively impacting disease progression.
Link to the article: rb.gy/gr77
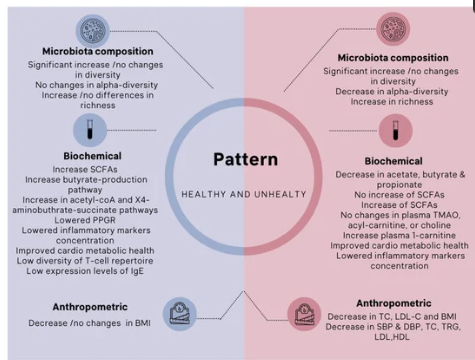
the influence of vegan/vegetarian diets on gut microbiota composition and biochemical and anthropometric levels in the healthy and unhealthy (metabolic and autoimmune disturbed) subjects.

Published On: 31/03/2023