💡 This meta-analysis and systematic review aimed to provide a comprehensive assessment of gut microbiota differences between individuals with depressive disorder and healthy controls.
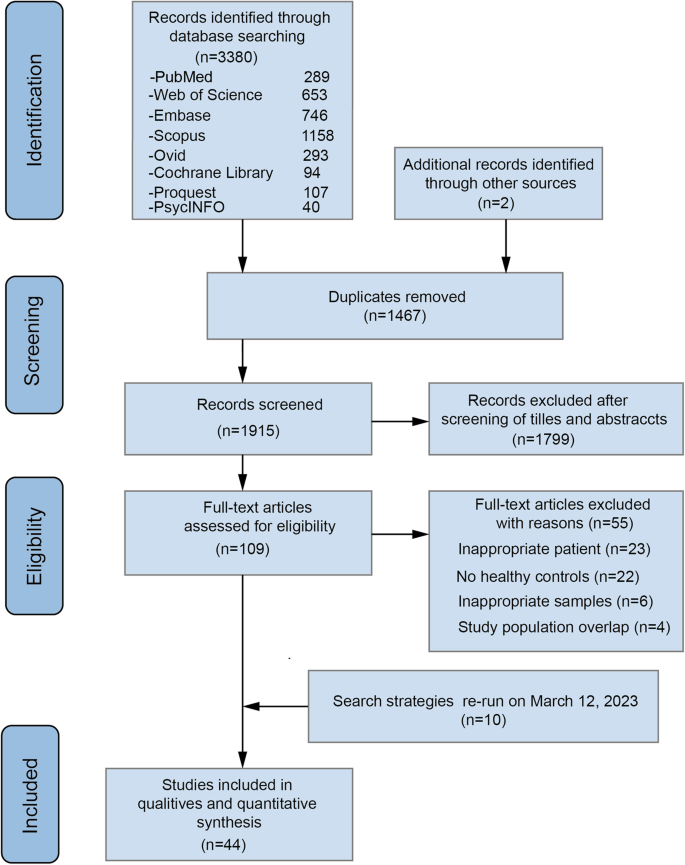
The study incorporated data from 44 studies, representing 2091 patients and 2792 controls, and employed rigorous methodologies, including meta-analyses, meta-regression, and subgroup analyses.
The study also explored potential influencers, such as geographic variations, medication use, age, sex, BMI, and depression severity.
📍 Methods:
a. Literature Search: PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Scopus, Ovid, Cochrane Library, ProQuest, and PsycINFO were systematically searched from database inception to March 07, 2022, with an update on March 12, 2023.
b. Inclusion Criteria: Studies comparing gut microbiota between individuals with depressive disorder and healthy controls were included.
c. Meta-Analyses: Pooled effect sizes (Standardized Mean Difference [SMD]) were calculated for alpha diversity indices, Firmicutes, and Bacteroidetes, utilizing a random-effects model.
d. Subgroup Analyses: Regional variations, medication status, and other relevant variables were explored as potential sources of heterogeneity.
e. Meta-Regression: Variables including age, sex, BMI, medication use, and depression severity were assessed for their impact on heterogeneity.
📍 Key Findings:
📌 Alpha Diversity and Phylum Levels:
i. No significant differences in alpha diversity indices, 𝘍𝘪𝘳𝘮𝘪𝘤𝘶𝘵𝘦𝘴, 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘉𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘰𝘪𝘥𝘦𝘵𝘦𝘴 were observed between depressive disorder and healthy control groups.
ii. Subgroup analyses revealed regional variations influencing Chao1 levels, with the West exhibiting lower diversity.
📌 Specific Taxonomic Alterations:
i. 𝘉𝘶𝘵𝘺𝘳𝘪𝘤𝘪𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴, 𝘊𝘰𝘱𝘳𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴, 𝘍𝘢𝘦𝘤𝘢𝘭𝘪𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘶𝘮, and others were consistently depleted, while 𝘌𝘨𝘨𝘦𝘳𝘵𝘩𝘦𝘭𝘭𝘢, 𝘌𝘯𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴, 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘚𝘵𝘳𝘦𝘱𝘵𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴 were enriched in depressive disorder.
ii. Meta-regression analysis failed to explain 100% of heterogeneity, suggesting the presence of unmeasured moderators.
📌 Influencing Factors:
i. Psychotropic medication and dietary habits were identified as potential influencers on gut microbiota composition.
ii. Subgroup meta-analysis indicated decreased Firmicutes and increased Bacteroidetes in medication-free patients.
📍 This study provides robust evidence of distinct gut microbiota composition in depressive disorder, characterized by decreased anti-inflammatory butyrate-producing bacteria and enrichment of pro-inflammatory genera. Influencing factors such as psychotropic medication and dietary habits should be considered in future research.
Link to the article: https://tinyurl.com/25daxb4h