💡 Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a chronic inflammatory skin condition, shares clinical similarities and inflammatory pathways with Crohn’s Disease (CD). This study compares the fecal microbiota and habitual diet of individuals with HS, CD patients, and controls to unravel potential links between gut dysbiosis, diet, and disease development.
📍 Associations between HS and CD suggest shared etiological factors. The Western diet has been linked to increased inflammatory diseases, yet the interplay of gut microbiota and diet in HS and CD remains unexplored. This study investigates the fecal microbiota and diet patterns in HS and CD, shedding light on potential biomarkers and risk factors.
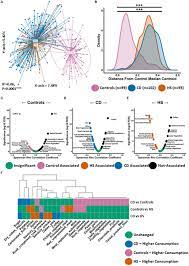
📍 Fecal microbiota composition was assessed through 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing in HS (n=55), CD (n=102), and control subjects (n=95). Dietary habits were analyzed to identify patterns and associations. Previously reported data on HS microbiota was reanalyzed, and new insights into diet patterns and microbiota composition were investigated.
📍 Key Findings:
📌 Dietary Similarities: Patients with HS exhibited a Western diet similar to CD patients, differing significantly from controls. High consumption of sugars and saturated fats characterized the diet in both HS and CD subjects.
📌 Microbiota Configuration: In HS, 40% of individuals displayed a microbiota configuration similar to CD, marked by an enrichment of pathogenic genera 𝘌𝘯𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘰𝘤𝘰𝘤𝘤𝘶𝘴, 𝘝𝘦𝘪𝘭𝘭𝘰𝘯𝘦𝘭𝘭𝘢, 𝘌𝘴𝘤𝘩𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘤𝘩𝘪𝘢, 𝘚𝘩𝘪𝘨𝘦𝘭𝘭𝘢) and depletion of beneficial genera (𝘍𝘢𝘦𝘤𝘢𝘭𝘪𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘦𝘳𝘪𝘶𝘮). The remaining 60% had a microbiota resembling controls.
📌 Antibiotic Influence: Antibiotic usage, common in HS treatment, correlated with distinct microbiota compositions. Notably, antibiotic use associated with lower abundance of health-associated microbiota.
📌 Inflammatory Markers: Individuals with HS exhibiting a CD-like microbiota configuration showed lower levels of the anti-inflammatory protein Gas6. Negative correlations were observed between health-associated genera and the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-12, implying increased inflammation in this subgroup.
📌 Dietary Covariates: Cardiovascular drug consumption, particularly ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, angiotensin II receptor antagonists, aspirin, and statins, correlated with microbiota variations in HS. Higher carbonated soft drink intake, linked to increased CD risk, was noted in individuals with a CD-like microbiota in HS.
📍 This research underscores the importance of understanding microbiota and diet patterns in HS and their potential implications for CD susceptibility. The identification of specific microbiota configurations and dietary associations provides insights into disease mechanisms, serving as a basis for future prospective studies and interventions targeting gut dysbiosis in HS.
Link to the Article : https://tinyurl.com/yd8xnuuh