💡 This study investigates the impact of acute high-altitude hypoxia on gut microbiota and intestinal structure in Sprague–Dawley rats and examines the potential protective effects of oxygen enrichment.
📌 The results demonstrate that acute hypoxia leads to intestinal injury, disrupting the morphological structure of the gut and altering gut flora.
Notably, oxygen enrichment significantly mitigates intestinal damage and restores the gut microbiota’s richness, diversity, and composition, indicating its potential as a therapeutic intervention at high altitudes.
📍 Methods:
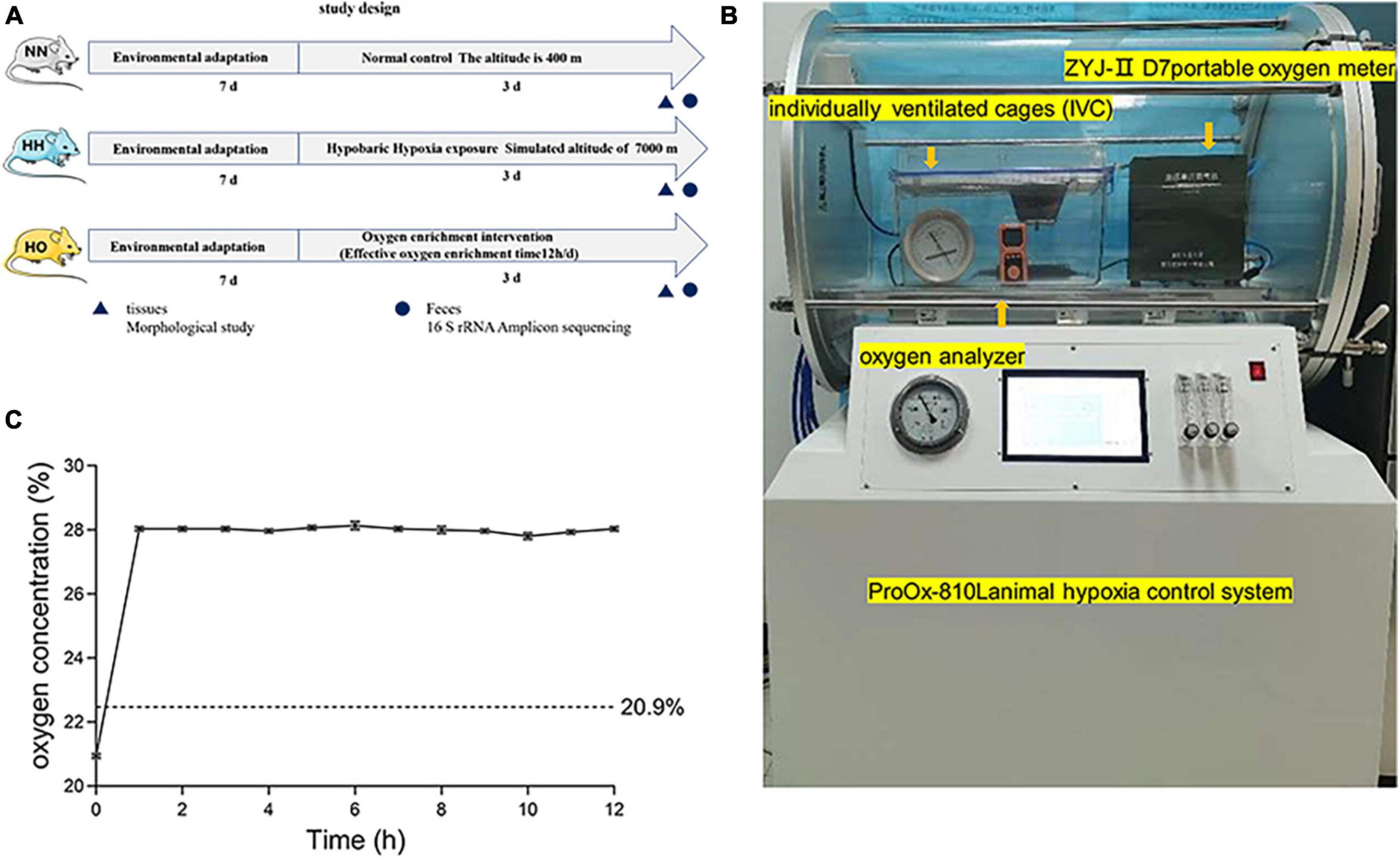
📌 Eighteen male Sprague–Dawley rats were divided into three groups: control (NN), hypobaric hypoxic (HH), and oxygen-enriched (HO). The HH group was exposed to simulated high-altitude hypoxia (7,000 m) for 3 days, while the HO group received oxygen enrichment for 12 hours daily.
Gut microbiota and intestinal structure were analyzed using high-throughput 16S rRNA gene sequencing and morphological assessments.
⭕ Key Findings:
📌 Acute high-altitude hypoxia induced severe structural damage to the colon tissue, including a reduction in crypt depth, epithelial cell shedding, and decreased goblet cell count, indicating intestinal injury.
📌 Gut microbiota composition analysis revealed an altered ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes and changes in specific genera like 𝘓𝘢𝘤𝘵𝘰𝘣𝘢𝘤𝘪𝘭𝘭𝘶𝘴 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘗𝘳𝘦𝘷𝘰𝘵𝘦𝘭𝘭𝘢𝘤𝘦𝘢𝘦𝘕𝘒3𝘉31 group in response to hypoxia.
📌 Oxygen enrichment significantly mitigated intestinal injury, as evidenced by increased crypt depth, intact epithelial cell morphology, and enhanced goblet cell density compared to the HH group.
📌 Oxygen enrichment also positively influenced gut microbiota, promoting higher richness, evenness, and diversity. It restored the balance of Bacteroidetes and Prevotellaceae, crucial microbiota at high altitudes.
Functional analysis indicated that oxygen enrichment affected metabolic pathways related to energy metabolism, amino acid metabolism, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle, potentially aiding in metabolic resilience during hypoxia.
📍 This study demonstrates the protective effects of oxygen enrichment on gut microbiota and intestinal structure in response to acute high-altitude hypoxia. Oxygen enrichment mitigates intestinal injury and helps restore gut microbiota richness and diversity, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic intervention to counteract hypoxic damage at high altitudes.
Link to the article: https://tinyurl.com/259v3nxf