💡Researchers discuss the roles of distinct types of gut-innervating neurons in the modulation of intestinal mucosal immunity and the therapeutic potential of strategies targeting neuroimmune crosstalk for intestinal diseases.
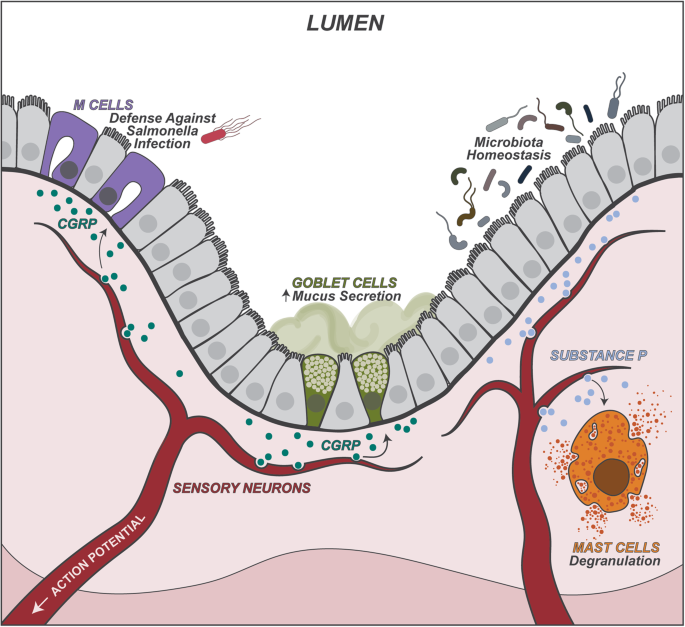
📌 The primary function of the gastrointestinal tract is food processing and digestion. As such, it is densely innervated by peripheral neurons, including sensory and autonomic neurons, that coordinate the detection of nutrients, gut motility, and the secretion of enzymes necessary for proper digestive functions. The Gastrointestinal tract is also populated by a myriad of immunocytes, including both innate and adaptive immune cells, which critically mediate gut tissue homeostasis and host defense against enteric pathogens.
📌 The microbiome also plays a critical role in regulating neuronal activation and immune development. Given that both immune cells and neurons can sense microbes directly or indirectly, the composition of the microbiome plays a critical role in neuronal programming or maturation to modulate visceral pain, gut motility, and other aspects of intestinal physiology.
📌 The brain receives and integrates ascending sensory signals from the gut and transduces descending signals back to the gut via autonomic neurons. Neurons regulate intestinal immune responses through the action of local axon reflexes or through neuronal circuits via the gut-brain axis. This neuroimmune crosstalk is critical for gut homeostatic maintenance and disease resolution.
📌 Therapeutic targeting of neurotransmitters and neuropeptide receptor signaling is an approach to apply neuroimmune principles to treat disease. Medications such as beta-adrenergic receptor antagonists (beta-blockers) developed to treat hypertension, angina pectoris, and cardiac arrhythmias or CGRP receptor antagonists used to treat migraine can be repurposed for gastrointestinal dysfunction interference by virtue of their ability to modulate gut immunity.
🔴 Researchers in this study focus on mechanisms underlying the neuronal regulation of inflammation and immunity in the gut and discuss how neurons and neurotransmitters are involved in immune responses during tissue repair and host defense.
Link to the article : go.nature.com/44bjh5Z
Published On: /06/2023