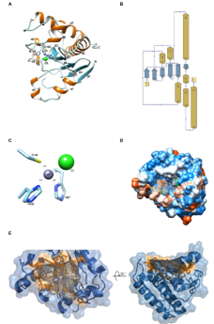
The discovery of new antibiotics and effectiveness of old ones have been continuously declining, suggesting that antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has important health and economic dangers both at the individual and population levels. The World Health Organization (WHO) considers that the ESKAPE family of pathogens is a leading cause of hospital-acquired infections worldwide. Peptidoglycan-degrading enzymes, also known as enzybiotics, are useful bactericidal agents in the fight against resistant bacteria. Authors in this study, identified a putative cell-wall lytic enzyme (EfAmi1) with predictive amidase activity in the prophage sequence integrated into the Enterococcus faecium 11C6_DIV0699 genome and characterized. Further, the crystal structure of EfAmi1 was determined and the key amino acid residues involved in substrate binding or catalysis were predicted and discussed.
Link to the article: bit.ly/43dx5MY
Published On: /05/2023