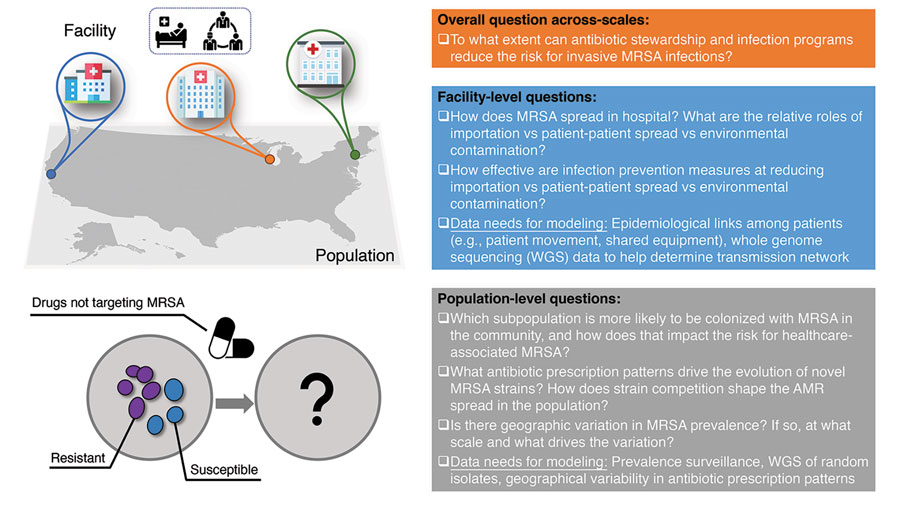
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a leading threat to global health. To limit the spread of antimicrobial-resistant organisms (AMROs) and reduce AMR-related disease burden, improved predictive intelligence is required to better estimate the emergence and spread of AMR within populations and healthcare facilities. Forecasting at the population level aims to predict the trend of infection or carriage prevalence in the general population for relatively long periods of months to years. For AMR pathogens, the forecast target might be the number of AMR infections or the proportion of isolates exhibiting resistance. Real-time infectious disease forecasting aims to generate estimations of future disease incidence at the population or community level. AMRO prediction has its own set of challenges, including wide and prolonged asymptomatic carriage, longer time scales, continuing evolution due to strain competition and antimicrobial drug use, and poorly observed disease burden. Authors in this study, discuss the potential for AMRO forecasting at the population and facility scales, highlighting challenges for this field, and suggest future research priorities.
Link to the article : bit.ly/3mUPezM
Published On: /04/2023