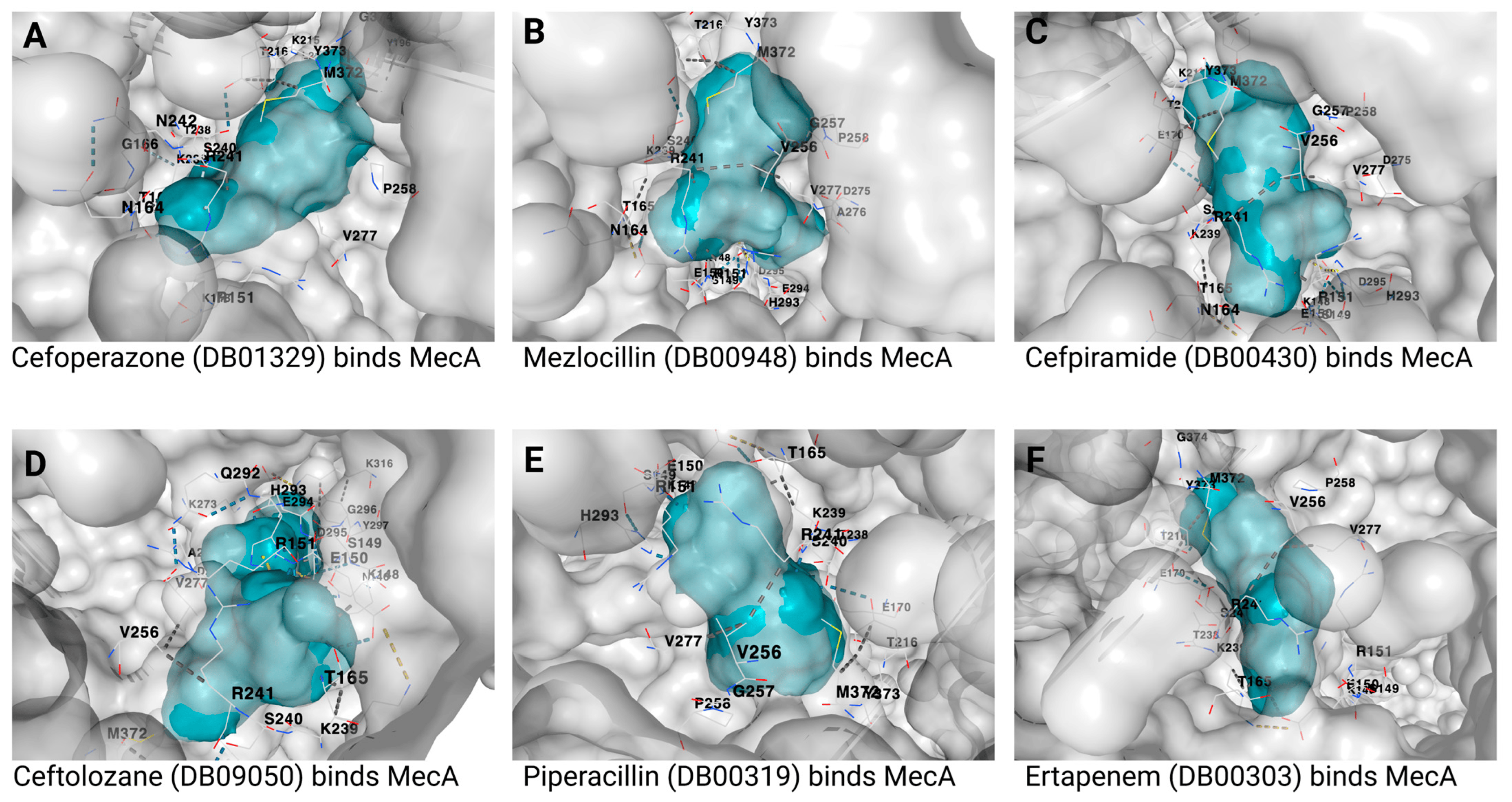
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is a dangerous pathogenic strain of Staphylococcus aureus, the most challenging to treat due to its high virulence and resistance to certain antibiotics. MRSA strains have an altered penicillin-binding protein, encoded by an acquired gene,mecA,, which is found in various bacterial species. In this work, the authors tried to identify approved antibiotics that can inhibit the mecA,antibiotic resistance gene found in MRSA strains. Two approaches were used: a protein sequence search and a structural similarity approach, followed by molecular docking experiments. This indicated that six drugs had a high binding affinity to the mecA antibiotic resistance gene. A key discovery from this research was that the antibiotic compound afamelanotide showed promising efficacy for treating MRSA infection and other related bacterial diseases because of its high affinity for mecA proteins.
Link to the article: rb.gy/cvz7
Published On: /04/2023