💡 This research focuses on identifying the associations between beta-lactam pharmacokinetic/ pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) targets and the emergence of resistance in Gram-negative bacteria in patients. The alarming rate of antimicrobial resistance demands strategies to mitigate this problem.
📌 Beta-lactams are the most widely used antibiotics, but their resistance is worrying, given their broad efficacy and safety profile.
📌 The study involved the collection of retrospective data between 2016 to 2019. Adult patients with two Gram-negative isolates receiving cefepime, meropenem, or piperacillin-tazobactam and had plasma beta-lactam concentrations were included in the study. Multiple regression analysis was used to examine the impacts of PK/PD parameters on resistance emergence.
1. Pseudomonas aeruginosa was found to be significantly associated with bacterial resistance emergence.
2. The mean daily ƒ AUC/MIC ≥ 494 was associated with a decreased risk of resistance development in Gram-negative infections.
3. Patients achieving a mean daily ƒ AUC/MIC ≥ 494 had a significantly shorter time on antibiotic therapy.
4. Out of the entire patients sample, only 31% of patients were able to meet the ƒ AUC/MIC ≥ 494 target.
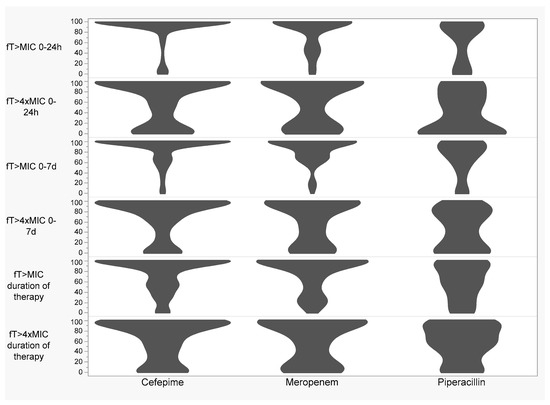
5. No association was found between time over Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (ƒ T > MIC) and time over four times the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (ƒ T > 4 × MIC) and the emergence of Gram-negative resistance.
6. The researchers estimated protein binding values to calculate the unbound fraction as total drug concentrations were measured, which might affect the results.
7. The study concludes that optimizing daily beta-lactam ƒ AUC/MIC exposure may help to minimize Gram-negative resistance and the duration of therapy.
📌 This paper is a critical contribution to the fight against antibiotic resistance, a pressing global public health concern. By shedding light on the relationship between the beta-lactam PK/PD targets like ƒ AUC/MIC and the development of resistance in Gram-negative bacteria, it adds to our understanding of how to best use these widely-prescribed antibiotics to ensure their continued efficacy.
📌 Additionally, it provides valuable insights on the importance of individual patient factors in determining the success of antibiotic treatment. The findings could lead to optimized dosage strategies for patients, ensuring effective treatment while minimizing resistance emergence. This careful balance between therapeutic effectiveness and prevention of resistance is the key to preserving the utility of our existing antibiotics, which makes this paper a valuable asset in the field of infectious diseases and antibiotic stewardship strategies.
Link to the article : https://tinyurl.com/3j2e8776