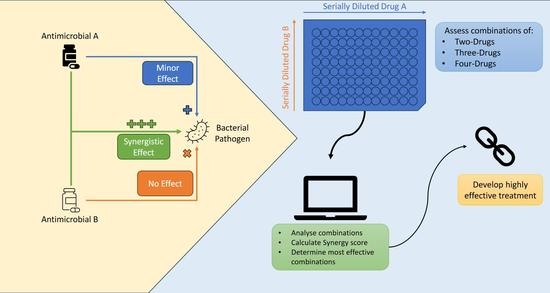
💡 This study investigates the potential of using combinations of four antimicrobial bioactive—silver nitrate, nisin, chitosan, and zinc oxide—for effective treatment of antimicrobial-resistant bacteria.
📌 The study aims to characterize the synergistic interactions of these bioactive compounds in two-, three-, and four-drug combinations against the bacteria 𝘌. 𝘤𝘰𝘭𝘪, 𝘚. 𝘢𝘶𝘳𝘦𝘶𝘴, 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘚. 𝘦𝘱𝘪𝘥𝘦𝘳𝘮𝘪𝘥𝘪𝘴
📌 The authors used a checkerboard assay, based on a broth microdilution protocol, which was used to measure the growth inhibition of the bacteria. Synergy scores, calculated using the Bliss Synergy model, were then used to determine the effectiveness of each combination.
📌 The study revealed that combinations of two to four bioactive compounds increasingly inhibited bacterial growth, displaying significant synergistic effects, particularly noted in the AgNO3-Chitosan combination.
📍 AgNO3 and Chitosan showed good synergistic interactions against each bacterial strain.
📍 AgNO3 and Nisin also demonstrated a number of highly synergistic combinations.
📍 In a three-drug combination, Chitosan, AgNO3, and nisin reported moderate-to-high synergy in growth inhibition against all the tested bacterial species.
📍 The four-drug combinations of chitosan, nisin, AgNO3, and zinc oxide yielded more effective results against bacterial species 𝘌. 𝘤𝘰𝘭𝘪, 𝘚. 𝘢𝘶𝘳𝘦𝘶𝘴, 𝘢𝘯𝘥 𝘚. 𝘦𝘱𝘪𝘥𝘦𝘳𝘮𝘪𝘥𝘪𝘴 when compared to the effect of each compound used individually.
📌 The most effective four-drug combination was able to cause complete inhibition against all tested bacterial strains with lesser amount of each bioactive compound than when used alone.
📌 This research concluded that combinational use of these four bioactive antimicrobial compounds presented a promising solution to counteract bacterial growth. The four-drug combination demonstrated higher efficiency in bacterial inhibition than when these compounds were used independently, indicating the potential for these substances to be used in treating bacterial infections more effectively.
📌 This research underscores the role of antimicrobial stewardship in optimizing the use of antimicrobials. It highlights the potential of combining antimicrobial bioactives to enhance patient outcomes, decrease microbial resistance, and curb multidrug-resistant infections. The study aligns with stewardship goals by identifying combinations that inhibit bacterial growth at lower drug concentrations.
Link to the article : https://tinyurl.com/2ftfvakh