💡 This study aimed to investigate the neuroprotective potential of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside (C3G), a prevalent anthocyanin in human diets, against TMT-induced neurodegeneration and cognitive impairment.
📌 The study sheds light on the multifaceted mechanisms underlying the neuroprotective effects of C3G and its interaction with the gut-brain axis.
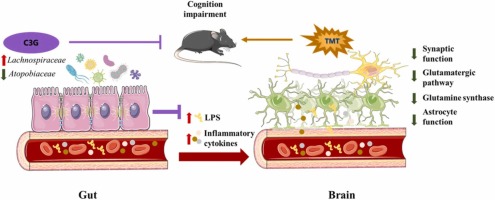
📌 Trimethyltin chloride (TMT) is a potent neurotoxin known for its ability to induce neurodegeneration, particularly in the hippocampus. This research explores the potential of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside (C3G), a common dietary anthocyanin, in mitigating TMT-induced neurotoxicity.
📍 Methods:
Animal Model: Mice were administered C3G (at two doses, 5 or 50 mg/kg) for 16 days, with a single intraperitoneal injection of TMT (2.7 mg/kg) on the eighth day.
Neurobehavioral Assessment: Cognitive function and the severity of TMT-induced seizures were evaluated in the mice.
Histopathological Analysis: Hippocampal neurodegeneration and dendritic spine loss were examined.
Metabolomics Analysis: Untargeted metabolomics was performed on mouse hippocampus samples to assess the effects of TMT exposure and C3G treatment on glutamate homeostasis.
Gut Microbiota Analysis: The relative abundance of gut microbial taxa was determined, and its association with inflammation and astrocyte dysfunction was investigated.
📍 Key Findings:
Neuroprotective Effects of C3G: Exposure to TMT resulted in seizures, cognitive impairment, neurodegeneration, and dendritic spine loss in the hippocampus. Administration of C3G, particularly at the higher dose (50 mg/kg), significantly mitigated these TMT-induced effects.
Restoration of Glutamate Homeostasis: TMT exposure disrupted glutamate homeostasis in the hippocampus, as indicated by changes in glutamic acid and glutamine levels. C3G treatment restored glutamate homeostasis by preserving the expression of glutamine synthetase (GS), particularly in astrocytes.
Modulation of Gut Microbiota: TMT exposure led to an increase in Atopobiaceae in the gut microbiota, accompanied by elevated levels of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and proinflammatory cytokines in the bloodstream. C3G reduced the relative abundance of Atopobiaceae while promoting the growth of protective gut commensal strains from the Lachnospiraceae family. This modulation of the gut microbiota correlated with reduced systemic inflammation.
Astrocyte Dysfunction and Gut-Brain Axis: TMT-induced astrocyte dysfunction, characterized by overexpression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and proinflammatory molecules, was observed. This astrocyte dysfunction was associated with alterations in the gut microbiota and systemic inflammation. C3G appeared to protect astrocyte function, potentially through its effects on gut microbiota and metabolites.
📌 TMT exposure led to neurodegeneration, cognitive impairment, dendritic spine loss, and disrupted glutamate homeostasis in the hippocampus. C3G effectively mitigated these neurotoxic effects, demonstrating its neuroprotective potential.
The restoration of glutamate homeostasis by C3G was associated with the maintenance of GS expression in astrocytes. Furthermore, C3G exhibited a modulatory effect on gut microbiota, particularly by reducing 𝘈𝘵𝘰𝘱𝘰𝘣𝘪𝘢𝘤𝘦𝘢𝘦 and promoting 𝘓𝘢𝘤𝘩𝘯𝘰𝘴𝘱𝘪𝘳𝘢𝘤𝘦𝘢𝘦, which contributed to a decrease in systemic inflammation. Astrocyte dysfunction appeared to be linked to alterations in gut microbiota and systemic inflammation, and C3G seemed to protect astrocyte function through these mechanisms.
Read The Article : https://tinyurl.com/2mek2d6r